Archived Content
The National Institute of Mental Health archives materials that are over 4 years old and no longer being updated. The content on this page is provided for historical reference purposes only and may not reflect current knowledge or information.
NIH-funded Brain Atlas Offers Clues to Psychiatric Disorders
• Press Release
A comprehensive three-dimensional atlas of the developing human brain that incorporates gene activity along with anatomical reference atlases and neuroimaging data has released its first major report online today in Nature. This National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded resource, freely available to the public, enables researchers to answer questions related to the early roots of brain-based disorders such as autism and schizophrenia.
This big science endeavor, which highlights the transcriptome—when and where genes are turned on in the brain— and anatomy of the human brain during mid-term pregnancy, was undertaken at the Allen Institute for Brain Science in Seattle. It is the first installment of a consortium project funded by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), part of the NIH, called the BrainSpan Atlas of the Developing Human Brain, which aims to profile gene activity throughout the course of brain development.
“Many neuropsychiatric diseases are likely the result of abnormal brain development during prenatal life,” said lead author Ed Lein, Ph.D., of the Allen Institute. "An anatomically precise molecular atlas of the brain during this time period is a first step to understanding how the human brain develops normally and what can go wrong.”
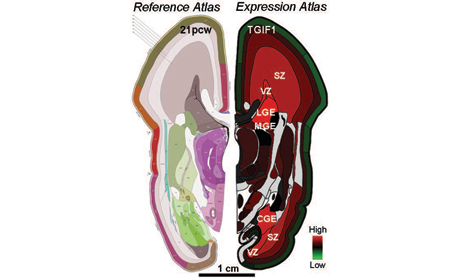
Source: Allen Brain Atlas
Although animal studies have provided invaluable insights in the basic mechanisms of brain function, there are limitations that make studies based on human tissues, which are very difficult to obtain, incredibly important. One key area is the neocortex, the outermost brain region involved in higher functions such as action and thought. The neocortex is smooth in rodents; in humans and non-human primates, it is much more complexly organized, elaborately folded into grooves and wrinkles called sulci and gyri.
Further differences in developmental compartments of this area exist between humans and non-human primates. The aim of this highly detailed atlas was to analyze all genes at this level of granularity, allowing meaningful analysis of the molecular underpinnings of human cortical development. Many psychiatric disorders show altered gene activity in the cortex, possibly highlighting changes that occurred during development of this region.
Lein and other researchers studied four donated, intact, high-quality human prenatal brains from preterm stillbirths—two from 15–16 weeks and two from 21 weeks post-conception – as a framework for their atlas. Contributing labs provided data from a variety of genomic and imaging techniques.
The BrainSpan Atlas aims to inspire new hypotheses regarding human brain development, and has already led to some surprising findings. For example, the study authors found significant differences between mouse and human brains in the subplate zone, a developmentally transient structure critical for proper cortical development. On the other hand, the researchers expected to find a unique molecular signature for the outer portion of the subventricular zone, an area which is not found in mice and which contains a hugely expanded pool of neuronal stem cells that give rise to our greatly expanded neocortex. Surprisingly, despite its much larger size, no significant differences were found between this zone and the inner portion of this layer that is conserved from mouse to human.
“The BrainSpan Atlas becomes very powerful when one can understand where and when a particular gene is used—for instance, is it active in precursor cells or in the neurons derived from them?” said Lein, who gave the example that autism candidate genes are expressed very early in in the cortex. Knowledge of the time and location of these genes may lead to future treatment targets and early interventions for this brain disorder, he added.
The BrainSpan Atlas already is making inroads in research surrounding human brain development and disease.
“Although the many genes associated with autism and schizophrenia don’t show a clear relationship to each other in the adult brain, the BrainSpan Atlas reveals how these diverse genes are connected in the developing brain,” said NIMH Director Thomas R. Insel, M.D. “Findings of what goes on early in the prenatal brain can lead to the development of biomarkers for diagnosing brain disorders and for matching patients to treatment options most likely to be successful.
“This atlas is a clear example of the progress that can be made when the public and private sectors work together,” Insel said. “On this first anniversary of the BRAIN Initiative, we are encouraged to see the impact the BrainSpan Atlas is already making on brain research.”
The resource is freely available for viewing, searching, and data mining for gene activity patterns as part of the BrainSpan Atlas of the Developing Human Brain (http://brainspan.org ), and can also be found via the Allen Brain Atlas data portal (http://www.brain-map.org).
Reference
Transcriptional landscape of the prenatal human brain. Miller JA, Ding S-L, Sunkin SM, Smith KA, Ng L, Szafer A, Ebbert A, Riley ZL, Aiona K, Arnold JM, Bennet C, Bertagnolli D, Brouner K, Butler S, Caldejon S, Carey A, Cuhaciyan C, Dalley RA, Dee N, Dolbeare TA, Facer BAC, Fend D, Fliss TP, Gee G, Goldy J, Gourley L, Gregor BW, Gu G, Howard RE, Jochim JM, Kuan CL, Lau C, Lee C-K, Lee F, Lemon TA, Lesnar P, McMurray B, Mastan N, Mosqueda NF, Naluai-Cecchini T, Ngo N-K, Nyhus J, Oldre A, Olson E, Parente J, Parker PD, Parry SE, Player AS, Pletikos M, Reding M, Royall JJ, Roll K, Sandman D, Sarreal M, Shapouri S, Shapovalova NV, Shen EH, Sjoquist N, Slaughterbeck CR, Smith M, Sodt AJ, Williams D, Zöllei L, Fischl B, Gerstein MB, Geschwind DH, Glass IA, Hawrylycz MJ, Hevner RF, Huang H, Jones AR, Knowles JA, Levitt P, Phillips JW, Sestan N, Wohnoutka P, Dang C, Bernard A, Hohmann JG, Lein ES. Nature , April 2, 2014.
Grants
About the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): The mission of the NIMH is to transform the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses through basic and clinical research, paving the way for prevention, recovery and cure. For more information, visit the NIMH website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit the NIH website .
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
