Archived Content
The National Institute of Mental Health archives materials that are over 4 years old and no longer being updated. The content on this page is provided for historical reference purposes only and may not reflect current knowledge or information.
Schizophrenia’s Strongest Known Genetic Risk Deconstructed
Suspect gene may trigger runaway synaptic pruning during adolescence – NIH-funded study
• Press Release
Versions of a gene linked to schizophrenia may trigger runaway pruning of the teenage brain’s still-maturing communications infrastructure, NIH-funded researchers have discovered. People with the illness show fewer such connections between neurons, or synapses. The gene switched on more in people with the suspect versions, who faced a higher risk of developing the disorder, characterized by hallucinations, delusions and impaired thinking and emotions.
“Normally, pruning gets rid of excess connections we no longer need, streamlining our brain for optimal performance, but too much pruning can impair mental function,” explained Thomas Lehner, Ph.D., director of the Office of Genomics Research Coordination of the NIH’s National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), which co-funded the study along with the Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research at the Broad Institute and other NIH components. “It could help explain schizophrenia’s delayed age-of-onset of symptoms in late adolescence/early adulthood and shrinkage of the brain’s working tissue. Interventions that put the brakes on this pruning process-gone-awry could prove transformative.”
The gene, called C4 (complement component 4), sits in by far the tallest tower on schizophrenia’s genomic “skyline” (see graph below) of more than 100 chromosomal sites harboring known genetic risk for the disorder. Affecting about 1 percent of the population, schizophrenia is known to be as much as 90 percent heritable, yet discovering how specific genes work to confer risk has proven elusive, until now.
A team of scientists led by Steve McCarroll, Ph.D. , of the Broad Institute and Harvard Medical School, Boston, leveraged the statistical power conferred by analyzing the genomes of 65,000 people, 700 postmortem brains, and the precision of mouse genetic engineering to discover the secrets of schizophrenia’s strongest known genetic risk. C4’s role represents the most compelling evidence, to date, linking specific gene versions to a biological process that could cause at least some cases of the illness.
“Since schizophrenia was first described over a century ago, its underlying biology has been a black box, in part because it has been virtually impossible to model the disorder in cells or animals,” said McCarroll. “The human genome is providing a powerful new way in to this disease. Understanding these genetic effects on risk is a way of prying open that block box, peering inside and starting to see actual biological mechanisms.”
McCarroll’s team, including Harvard colleagues Beth Stevens, Ph.D. , Michael Carroll, Ph.D. , and Aswin Sekar , report on their findings online Jan. 27, 2016 in the journal Nature.
A swath of chromosome 6 encompassing several genes known to be involved in immune function emerged as the strongest signal associated with schizophrenia risk in genome-wide analyses by the NIMH-funded Psychiatric Genomics Consortium over the past several years. Yet conventional genetics failed to turn up any specific gene versions there linked to schizophrenia.
To discover how the immune-related site confers risk for the mental disorder, McCarroll’s team mounted a search for “cryptic genetic influences” that might generate “unconventional signals.” C4, a gene with known roles in immunity, emerged as a prime suspect because it is unusually variable across individuals. It is not unusual for people to have different numbers of copies of the gene and distinct DNA sequences that result in the gene working differently.
The researchers dug deeply into the complexities of how such structural variation relates to the gene’s level of expression and how that, in turn, might relate to schizophrenia. They discovered structurally distinct versions that affect expression of two main forms of the gene in the brain. The more a version resulted in expression of one of the forms, called C4A, the more it was associated with schizophrenia. The more a person had the suspect versions, the more C4 switched on and the higher their risk of developing schizophrenia. Moreover, in the human brain, the C4 protein turned out to be most prevalent in the cellular machinery that supports connections between neurons.
Adapting mouse molecular genetics techniques for studying synaptic pruning and C4’s role in immune function, the researchers also discovered a previously unknown role for C4 in brain development. During critical periods of postnatal brain maturation, C4 tags a synapse for pruning by depositing a sister protein in it called C3. Again, the more C4 got switched on, the more synapses got eliminated.
In humans, such streamlining/pruning occurs as the brain develops to full maturity in the late teens/early adulthood – conspicuously corresponding to the age-of-onset of schizophrenia symptoms.
Future treatments designed to suppress excessive levels of pruning by counteracting runaway C4 in at risk individuals might nip in the bud a process that could otherwise develop into psychotic illness, suggest the researchers. And thanks to the head start gained in understanding the role of such complement proteins in immune function, such agents are already in development, they note.
“This study marks a crucial turning point in the fight against mental illness. It changes the game,” added acting NIMH director Bruce Cuthbert, Ph.D. “Thanks to this genetic breakthrough, we can finally see the potential for clinical tests, early detection, new treatments and even prevention.”
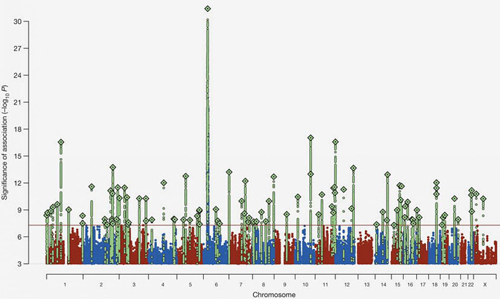
The site in Chromosome 6 harboring the gene C4 towers far above other risk-associated areas on schizophrenia’s genomic “skyline,” marking its strongest known genetic influence. The new study is the first to explain how specific gene versions work biologically to confer schizophrenia risk.
Source: Psychiatric Genomics Consortium
Reference
Sekar A, Biala AR, de Rivera H, Davis A, Hammond TR, Kamitaki N, Tooley K Presumey J Baum M, Van Doren V, Genovese G, Rose SA, Handsaker RE, Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, Daly MJ, Carroll MC, Stevens B, McCarroll SA. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature. Jan 27, 2016. DOI: 10.1038/nature16549.
Grants
MH10564, MH077139, HG006855, GM007753
About the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): The mission of the NIMH is to transform the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses through basic and clinical research, paving the way for prevention, recovery and cure. For more information, visit the NIMH website.
NHGRI is one of the 27 institutes and centers at the National Institutes of Health. The NHGRI Extramural Research Program supports grants for research, and training and career development at sites nationwide. Additional information about NHGRI can be found at www.genome.gov .
The National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) is a part of the National Institutes of Health that supports basic research to increase our understanding of biological processes and lay the foundation for advances in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. For more information on the Institute's research and training programs, visit www.nigms.nih.gov .
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit the NIH website .
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
