NIMH Intramural Research Program Response to COVID-19
NIMH COVID-19 Clinical Studies-Amend Maryland Pao, M.D.
Clinical & Deputy Scientific Director, NIMH
paom@mail.nih.gov
NIMH Joint Alliance-Coalition for Research Progress Town Hall
October 5th, 2020
NIMH Intramural Research Projects- COVID-19
Project Themes : Act early in response to public health emergency
- Methods development and harmonization
- Leverage NIMH existing research data
- Utilize online platforms for data collection
- Collaborate with intramural and extramural researchers
- Track changes over time using repeated measures
- Target specific populations (e.g., youth, parents, adults, health care workers)
NIMH COVID-19 Clinical Studies-Amend
Amended Studies
- Characterization and Treatment of Adolescent Depression (Stringaris)
- Characterization and Pathophysiology of Severe Mood and Behavioral Dysregulation in Children and Youth (Brotman)
- Fluoxetine's Effects on Attention and Emotional Memory in Anxious and Depressed Youth and Adults (Pine w/Brotman)
NIMH COVID-19 Clinical Studies-NEW
New Studies
- Mental Health Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on NIMH Research Participants and Volunteers (Chung)
- Mental Health Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Health Care Workers (Zarate/Park)
- Impact on Anxiety and Motivation of COVID-19 and Predictors of Individual Responses (Grillon/Ernst)
CoRonavIruS Health Impact Survey (CRISIS) 3.0
- Questionnaires developed through a collaborative effort between research teams of Kathleen Merikangas, Argyris Stringaris and Michael Milham (Child Mind Institute/NYSPI) and many other contributors
- Translated into 10 different languages internationally
- Several thousand surveys piloted and completed
- http://www.crisissurvey.org/
CoRonavIruS Health Impact Survey (CRISIS) 3.0

Characterization & Treatment of Adolescent Depression (CAT-D)
Amended Study NCT03388606
PI: Stringaris
- Protocol was the first to be approved to collect data on COVID-19 at NIMH
- Amongst the first to be approved to conduct telemedicine
- Assessments of COVID-19 related symptoms and mental health items on parents and young people in a longitudinal (i.e., repeated measures) study.
- Going through the 8th wave of data collection (979 assessments to date)
- On these participants, have collected:
- clinical questionnaires
- neurocomputational experimental tasks
- clinical interviews
- Significant clinical care has been provided since the onset of the pandemic through this protocol
Characterization & Treatment of Adolescent Depression (CAT-D)
Amended Study NCT03388606
PI: Stringaris
Results/Summary about depressive symptoms in adolescents
- Major Depressive Disorder n=106, Healthy Volunteers n=70
- First wave of repeat measures showed stable differences between groups
- A lot of interindividual variation
- No overall increase in depressive symptoms
- No apparent differences in worries about infection
- Possible differences in worries about physical and mental health overall
- Explanations? Pandemic and general lockdown (“we are all in this together”); measures done too early; families were home together
- More follow up in progress
Mental Health Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on NIMH Research Participants and Volunteers
New Study NCT04339790
PI: Chung
- Collaboration across NIMH IRP labs (Chung, Grillon, Zarate, Atlas, Ungerleider, McMahon) to invite previous study participants to enroll in this study
- Study participants must be 18 years or older and English-speaking; no exclusion criteria
- Study began in early April 2020 and collects repeated measures every two weeks of mental health symptoms, distress and COVID-19 psychosocial stressors
- Study has reached the 6-month end-of-study timepoint for first set of enrollees
- Will leverage NIMH patient and healthy volunteer clinical status – verified by Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 – to evaluate the COVID-19 stressor survey
- Using machine learning to predict the clinical status of the study population, many of whom report a history of mental illness (Pereira)
- Outreach effort to recruit more minority participants is underway
Mental Health Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on NIMH Research Participants and Volunteers
New Study NCT04339790
PI: Chung
Results/Summary:
- Enrolled more than 3,100 people from all 50 U.S. states
- 10% of the current sample have previously been evaluated for NIMH research studies
- 90% convenience sample of participants learned about the study based on a wide range of outreach efforts, e.g., listservs, social media, mental health advocacy organizations, clinicaltrials.gov and word of mouth
- Demographics of the study population through the first 5 months of the study: Mean age 46.3; 84% female; 90% white, 3% Black; 90% non-Hispanic; 82% bachelor’s degree or higher
- Limitations:
- enrollment may relate to comfort or time to complete online research surveys
- data are self-report (not verifiable) but nested sample of known NIMH volunteers and patients can help validate some study findings including a COVID-19 specific questionnaire developed for the study
Mental Health Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Health Care Workers
New Study
PI: Zarate
- All online survey study only that utilized a sample of convenience;
- Priority aims for this study were to initiate an all online survey study using new online techniques for consent and data gathering, and to quickly start collecting data during an intense period of the COVID-19 pandemic
- Study was not intended to be an epidemiological study and given the sampling method will have limitations with regard to generalization of results
Results/Summary:
- The enrollment period was approximately 1 month in May-June 2020. Enrollment has closed with 1300 individuals consenting for the study and over 900 filled out more than 3 of the survey instruments. Of the 900+ participants, 85% were women, mean age 44 years, with race/ethnicity skewed toward white/Caucasian populations
Impact on Anxiety and Motivation of COVID-19 and Predictors of Individual Responses
New Study NCT04377100
PI: Grillon and Ernst
- Recruits from general population and individuals who have previously participated in NIH studies, have been comprehensively clinically characterized, and taken part in fMRI studies; participants will be assessed again when the threat of the pandemic is significantly reduced
- Online questionnaires (on CTDB platform) and two online behavioral tasks, a motivation task (incentive-related finger tapping) and the standard attention-bias dot-probe task
Results/Summary:
- About 800 participants completed the study: 260 NIH participants (69 with an anxiety disorder, and 191 healthy), and 540 participants from the general population
- Compared to non-anxious, anxious individuals show: Weaker motivation to work for a reward (motivation task); Larger attention bias for threat stimuli (dot-probe task); More severe worrying and more physical complaints (COVID-19 survey)
- Trainees will present 6 posters at the NIMH Scientific Training Day
- Planned statistics to examine moderators of the effects of the COVID-pandemic on mental health. Such moderators include demographic (age, sex, SES, ethnicity) and clinical factors, as well as resilience, executive function capacity
Collaborating with NIAID on COVID-19 Research
In Progress NCT 044111147
- NIAID COVID-19 Survivor Study: A Longitudinal Study of COVID-19 Sequelae and Immunity (PI: M. Sneller)
- Adult men and women recovering from COVID-19 (n= up to 300) and their household contacts (n= up to 400) over next 3 years, followed at regular intervals every 6 months
- Mental health measures and evaluations provided by Dr. Joyce Chung, Dr. Haniya Raza, Dr. Onyi Okeke for a subset of sample (n=100) to understand the mental health symptoms in survivors including "long haulers"
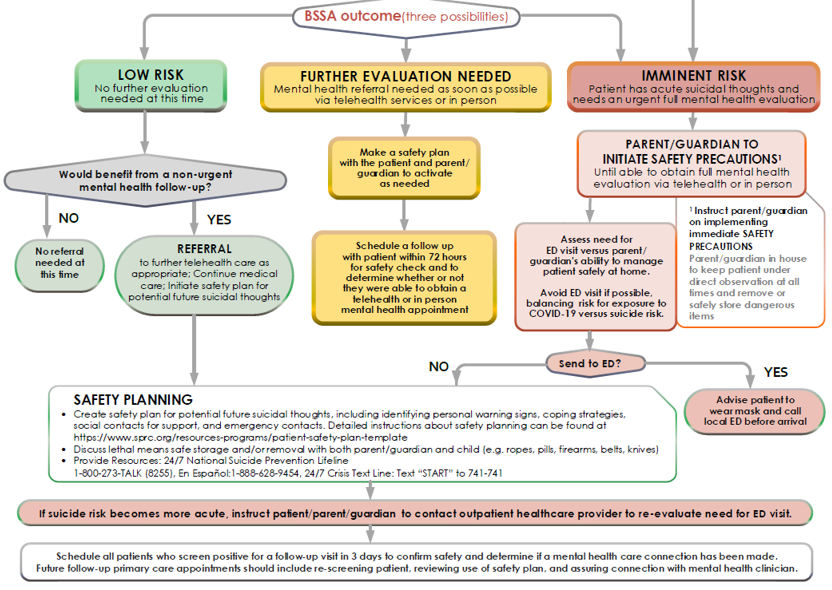
Ask Suicide Screening Questions (ASQ) MODIFIED DURING COVID-19 (Horowitz et al.)
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/research/research-conducted-at-nimh/asq-toolkit-materials/index.shtml
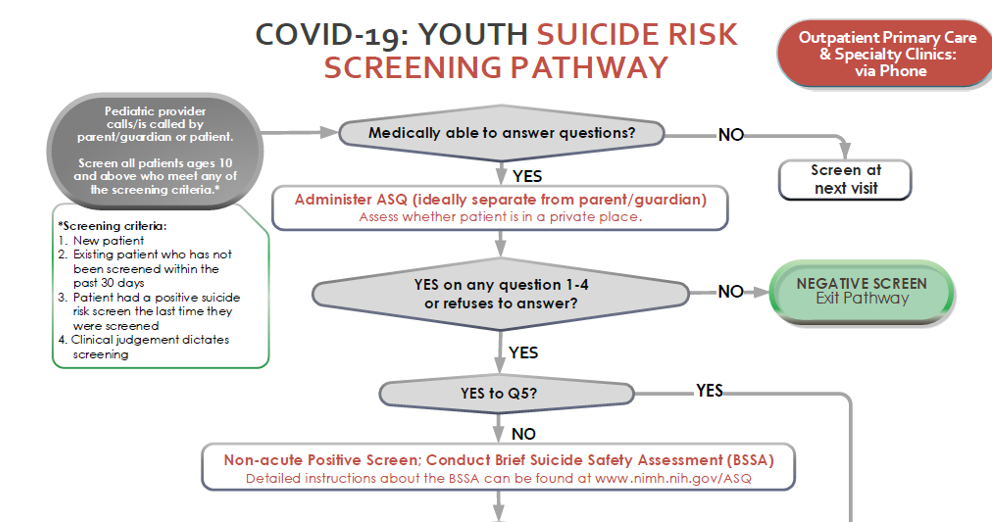
Ask Suicide Screening Questions (ASQ) MODIFIED DURING COVID-19 (Horowitz et al.)
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/research/research-conducted-at-nimh/asq-toolkit-materials/index.shtml
Mental Health Resources for NIH Staff During COVID-19 Pandemic with NIMH



Questions?


