Science Updates About Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Digital Autism Screening Tool Could Enhance Early Identification
-
A tablet-based screening tool that analyzes children’s behavior in response to specific video clips shows promise for enhancing early autism screening, according to a study supported by NIMH.
- Understanding the Underpinnings of Sensory Hypersensitivity in SCN2A-Associated Autism
-
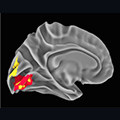
In this NIMH-supported study, researchers investigated the neural underpinnings of sensory hypersensitivity in SCN2A-associated autism.
- NIMH’s Dr. Susan Daniels Designated National Autism Coordinator
-
Susan A. Daniels, Ph.D. has been appointed as the HHS National Autism Coordinator and Director of the Office of National Autism Coordination (ONAC).
- Infants’ Health Record Data May Improve Early Autism Screening
-
Research supported by NIMH suggests that children’s health records may yield some promising insights that could improve the accuracy of early autism screening.
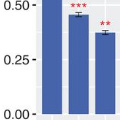
- Attention to Geometric Images May Offer Biomarker for Some Toddlers with Autism
-
An NIMH-supported study shows that preference for geometric images may be robust enough to serve as a biomarker for identifying some young children with autism.
- NIH Announces Winners of High School Mental Health Essay Contest
-
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is pleased to announce the winners of 2022 Speaking Up About Mental Health! This Is My Story essay contest.
- NIH Awards $100 Million for Autism Centers of Excellence Program
-
The National Institutes of Health has awarded a total of $100 million over the next five years to support nine Autism Centers of Excellence. This endeavor funds large research projects to understand and develop interventions for autism spectrum disorder.
- Toddlers’ Responses to “Baby Talk” Linked to Social, Cognitive, Language Abilities
-
In an NIMH-supported study, researchers found that toddlers respond to emotionally expressive speech in different ways, and these varied responses are linked with their social, linguistic, and cognitive abilities.
- Multistage Autism Screening in Early Intervention Settings May Reduce Disparities
-
An NIMH-supported study shows that incorporating a multistage screening process for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) into federally funded early intervention services may reduce disparities in early ASD diagnosis.
- Autism and Congenital Heart Disease Share Underlying Molecular Network
-
A recent study of gene networks may hold some promising clues about shared mechanisms underlying autism spectrum disorder and congenital heart disease, two physiologically distinct disorders that often co-occur.
- Machine Learning Study Sheds Light on Gaze Patterns in Adults With Autism
-
NIMH researchers examine what people with ASD and people without ASD look at when viewing a social scene.
- Acting National Autism Coordinator Named
-
National Autism Coordinator Ann E. Wagner, Ph.D., will retire from federal service on June 30, 2021—Susan A. Daniels, Ph.D., will serve as Acting National Autism Coordinator beginning on July 1, 2021, and until a permanent successor is named.
- Media Advisory: Prototype App for Mobile Devices Could Screen Children at Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder
-
A mobile app was successful at distinguishing toddlers diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) from typically developing toddlers based on their eye movements while watching videos, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health.
- Testing and Refining Biomarkers to Support Intervention Research for Children with Autism
-
NIMH, along with other NIH Institutes, is supporting the ABC-CT project, a multisite study that aims to test and refine biomarkers that can be used as objective measures of social impairment for children with autism in clinical trials, leading to more predictive and personalized treatment.
- Supporting the Development of Early Autism Screening Tools
-
NIMH, along with other NIH Institutes, is supporting the goal of identifying autism in the first year of life by funding projects that seek to seek to translate findings related to early-emerging signs of autism into practical ASD screening tools that can be implemented in the general population and community settings.
- Large-Scale Genetics Study Sheds Light on Developmental Origins of Autism
-
Researchers were able to identify different types of rare genetic variations associated with autism spectrum disorder by analyzing data shared via the NIMH-funded Autism Sequencing Consortium.
- NIH Awards Funding for Early Autism Screening
-
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded more than four million dollars in FY 2019 to support seven research projects aimed at developing and validating screening tools to detect signs of autism spectrum disorder in the first year of life.
- New Findings Reveal Surprising Role of the Cerebellum in Reward and Social Behaviors
-
A new study in rodents has demonstrated, for the first time, that the brain’s cerebellum plays a role in controlling reward and social preference behavior—findings that shed light on the brain circuits critical to the affective and social dysfunction seen across multiple psychiatric disorders.
- 2,000 Human Brains Yield Clues to How Genes Raise Risk for Mental Illnesses
-
PsychENCODE researchers are discovering the biological mechanisms by which mental illness risk genes work in the human brain.
- Inflammation in Pregnant Moms Linked to Child’s Brain Development
-
High levels of maternal inflammation during pregnancy have been linked to effects in children, including reduced brain circuit communications and altered long-distance brain wiring at birth, poorer cognitive function at one year – and to reduced impulse control and working memory at two years.
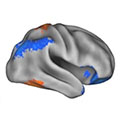
- “Covert” Neurofeedback Tunes-up the Social Brain in ASD
-
Young people with autism unknowingly tuned up flagging neural connections by playing a picture puzzle game that was rigged by their own brain activity.
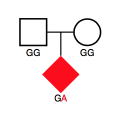
- Inherited Variations in Noncoding Sections of DNA Associated with Autism
-
A new study has identified an association between paternally-inherited rare structural variants in noncoding segments of genes and the development of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The study adds to a growing body of research describing genetic contributors to ASD.
- Suspect Molecules Overlap in Autism, Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder
-
Depression, schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder share some of the same patterns of suspect gene expression – molecular signatures.
- NIMH’s Dr. Ann Wagner Designated as the National Autism Coordinator
-
NIMH’s Dr. Ann Wagner has been designed as the National Autism Coordinator. In this role, she will play a vital role in ensuring the implementation of national autism spectrum disorder research, services, and support activities across federal agencies.
- Our Brains Harbor “Residual Echo” of Neanderthal Genes
-
Researchers have produced the first direct evidence that parts of our brains implicated in mental disorders may be shaped by a “residual echo” from our ancient past. The more a person’s genome carries genetic vestiges of Neanderthals, the more certain parts of his or her brain and skull resemble those of humans’ evolutionary cousins that went extinct 40,000 years ago.
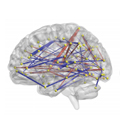
- Neuroimaging Technique May Help Predict Autism among High-Risk Infants
-
Functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging (fcMRI) may predict which high-risk, 6-month old infants will develop autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by age 2 years.
- Brain Circuit Tweak Wins Her Affection (if she’s a vole)
-
For the first time, neuroscientists have boosted a female rodent’s partnering with a male by stimulating connectivity of a brain reward circuit. Understanding the circuitry of such affiliative behaviors may lead to improved treatments for social impairment in severe mental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder.
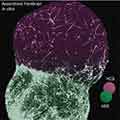
- Human Forebrain Circuits Under Construction – in a Dish
-
Neuroscientists have created a 3D window into the human brain’s budding executive hub assembling itself during a critical period in prenatal development.
- Delayed Walking May Signal Spontaneous Gene Anomalies in Autism
-
Researchers have discovered a pattern of genetic glitches and behavioral features, such as delayed walking, in some cases of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that could ultimately lead to identification of subgroups and improved treatment.
- A Third of Suspect Mutations in ASD Just “Noise”
-
Researchers have narrowed suspected genetic causes of autism and related developmental disabilities by ruling out what they call the “noise of benign variation.”
- Schizophrenia, Autism Risk Gene Trajectories Point to Shared Causes
-
Schizophrenia, autism risk gene trajectories point to shared causes