Science Updates
- Developing Tools for Measuring Mental Health Outcomes
-
The National Institutes of Health has funded six projects to develop, test, and validate outcome-focused quality measures for mental health, which are used to understand the impact of interventions when implemented in real-world health care systems and settings.
- How the Brain Creates New Memories While Maintaining Old Ones
-
A new study funded by the National Institutes of Health uncovered patterns in the activation of old and new memories during sleep that keep these memories separate.
- Predictive Models Show Promise in Preventing Suicide
-
In a study funded by the National Institutes of Health, researchers created new suicide risk prediction models using data in electronic health records from the Indian Health Service.
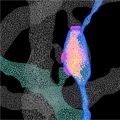
- Study Illuminates the Structural Features of Memory Formation at the Cellular and Subcellular Levels
-
In a study supported by NIMH, researchers revealed the structural underpinnings of memory formation across a broad network of neurons in the mouse brain.
- Study Illuminates the Genetic Architecture of Bipolar Disorder
-
Largest-ever genome-wide study of a diverse group of people with bipolar disorder sheds new light on the genetic architecture underlying the disorder.
- Dr. Sarah Hollingsworth Lisanby to Depart NIMH
-
Sarah Hollingsworth “Holly” Lisanby, M.D., Director of the Division of Translational Research, will depart NIMH this spring to join Arizona State University.
- Integrated Care for Depression Yields Extended Benefits, Malawi Study Shows
-
An NIMH-funded study showed that incorporating depression treatment into care for chronic health conditions improved well-being for both patients and their families.
- Primary Care Can Play Key Role in Suicide Prevention
-
Adding suicide care practices to routine adult primary care visits reduced suicide attempts by 25% in the months after the visit.
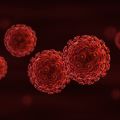
- Researchers Investigate Potential Treatment for Eliminating HIV from the Brain
-
In a recent NIMH-funded study, researchers explored a potential new way of clearing HIV from the brain by testing a drug that targets a type of immune cell known as macrophages.
- Brain Connectivity Linked With Cognition in People With Early Psychosis
-
An NIMH-funded study identified consistent links between brain connectivity and cognitive function in people with early stage psychosis and people at high risk who later developed psychosis.