Science Updates About Basic Research
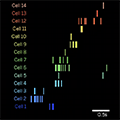
- How the Brain Creates New Memories While Maintaining Old Ones
-
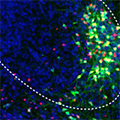
A new study funded by the National Institutes of Health uncovered patterns in the activation of old and new memories during sleep that keep these memories separate.
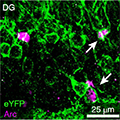
- Study Illuminates the Structural Features of Memory Formation at the Cellular and Subcellular Levels
-
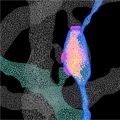
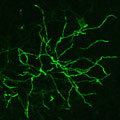
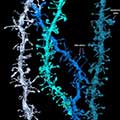
In a study supported by NIMH, researchers revealed the structural underpinnings of memory formation across a broad network of neurons in the mouse brain.
- Researchers Fully Map Neural Connections of the Fruit Fly Brain
-
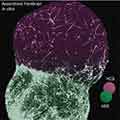
A scientific team supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) unveiled the first complete map of the neural connections of the common fruit fly brain.
- Scientists Map Networks Regulating Gene Function in the Human Brain
-
An NIMH-funded research consortium has produced the largest and most advanced multidimensional maps of gene regulation networks in the brains of people with and without mental disorders.
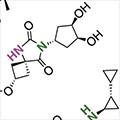
- Basic Research Powers the First Medication for Postpartum Depression
-
• 75th Anniversary
Decades of NIMH-supported basic research led to a pioneering treatment for postpartum depression and continues to power exciting advances in women's mental health care.
- Decades of Dedication and Collaboration: Unraveling the HIV Mystery
-
• 75th Anniversary
In celebration of NIMHs 75th anniversary, we reflect on decades of work by the institute to understand and eradicate HIV.
- Researchers Expand Understanding of Genetic Mechanisms Underlying Fragile X Syndrome
-
An NIMH-supported study of the 3D genome revealed widespread silencing of genes with important roles in brain function in fragile X syndrome and related disorders.
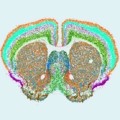
- Scientists Unveil Complete Cell Map of a Whole Mammalian Brain
-
For the first time ever, an international team of researchers has created a complete cell atlas of a whole mammalian brain.
- Scientists Unveil Detailed Cell Maps of the Human Brain and the Nonhuman Primate Brain
-
A group of international scientists have mapped the genetic, cellular, and structural makeup of the human brain and the nonhuman primate brain, allowing for a deeper knowledge of the cellular basis of brain function and dysfunction, helping pave the way for a new generation of precision therapeutics for people with mental disorders and other disorders of the brain.
- Blocking HIV Enzyme Reduces Infectivity and Slows Viral Rebound
-
In this NIMH-funded study, researchers developed a compound that blocked an enzyme critical for forming HIV particles, which stopped the virus from correctly forming and becoming infectious.
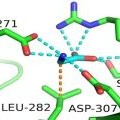
- Researchers Solve the Puzzle of a Brain Receptor’s Activation
-
Researchers in a NIMH-supported study identified a new receptor for glycine that helps enhance communication between nerve cells in the brain and offers a potential new target for treating mental disorders.
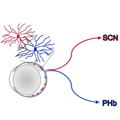
- Newly Discovered Brain Connection Affects Reward Behavior in Mice
-
NIMH-funded research sheds light on how negative early life experiences may impact how we act in response to rewards, which is often disrupted in people with mental illnesses.
- Researchers Find Order in the Language of the Brain
-
New research supported by NIMH used mathematical approaches to explain how neurons in the brain communicate over time to support information processing.
- Researchers Unlock Genetic Mutations Contributing to Disorders in the Brain
-
Researchers identified novel genes with mosaic mutations contributing to treatment-resistant pediatric epilepsy and pointing to specific disrupted pathways in cortical development.
- HIV Can Persist for Years in Myeloid Cells of People on Antiretroviral Therapy
-
A subset of white blood cells, known as myeloid cells, can harbor HIV in people who have been virally suppressed for years on antiretroviral therapy, according to findings from a small study supported by the National Institutes of Health.
- T Cells Help HIV Enter and Persist in the Brain
-
A recent NIMH-supported study sheds light on the role of a unique set of T cells in trafficking HIV infection into the brain and mediating the virus’ persistence there.
- Researchers Develop Method to Study Brain Connectivity, Functionality
-
Scientists have developed a research method that allows for a much more detailed examination of the brain processes involved in some neurological and mental disorders.
- Tool Uses Light to Inhibit Neural Activity in Mice
-
Researchers supported by NIH have developed a way to genetically insert a type of light receptor into neurons. The new technique enables the researchers to suppress the neuron’s activity using pulses of light.
- Autism and Congenital Heart Disease Share Underlying Molecular Network
-
A recent study of gene networks may hold some promising clues about shared mechanisms underlying autism spectrum disorder and congenital heart disease, two physiologically distinct disorders that often co-occur.
- Genomic Data From More Than 41,000 People Shed New Light on Bipolar Disorder
-
In the largest genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder to date, researchers found about twice as many genetic locations associated with bipolar disorder as reported in previous studies. These and other findings help improve our understanding of the biological origins of bipolar disorder.
- Mapping ‘Imbalance’ in Brain Anatomy Across the Lifespan
-
Researchers in the NIMH Intramural Research Program have developed a new way to measure the degree to which the proportions of an individual person’s brain differ from the proportions typically seen in the broader population. This technique yields new insights into brain development and offers tools for further study.
- New Experiences Enhance Learning by Resetting Key Brain Circuit
-
A study of spatial learning in mice shows that exposure to new experiences dampens established representations in the brain’s hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, allowing the mice to learn new navigation strategies.
- Gene Readouts Contribute To Distinctness of Mental Disorders
-
A new study conducted by researchers at NIMH suggests that differences in the expression of gene transcripts – readouts copied from DNA that help maintain and build our cells – may hold the key to understanding how mental disorders with shared genetic risk factors result in different patterns of onset, symptoms, course of illness, and treatment responses.
- NIH-funded Study Sheds Light on Abnormal Neural Function in Rare Genetic Disorder
-
A genetic study has identified neuronal abnormalities in the electrical activity of cortical cells derived from people with a rare genetic disorder called 22q11.2 deletion syndrome.
- Genetic Variations Highlight the Importance of Metabolic Processes in Anorexia
-
The need to identify effective targets for intervention in anorexia nervosa is pressing, as patient outcomes are often poor. An NIMH-funded genome-wide association study suggests that metabolic processes may play an important role in the disorder, offering a promising new avenue for investigation.
- Study Shows Highly Reproducible Sex Differences in Aspects of Human Brain Anatomy
-
A scientific analysis of more than 2,000 brain scans found evidence for highly reproducible sex differences in the volume of certain regions in the human brain.
- Brain Cells Can Harbor and Spread HIV Virus to the Body
-
Researchers funded by NIMH have found that astrocytes, a type of brain cell, can harbor HIV and then spread the virus to immune cells that traffic out of the brain and into other organs.
- New NIMH Strategic Plan Paves the Way for Advances in Mental Health Research
-
The Strategic Plan for Research advances the Institute’s mission and helps guide future mental health research efforts.
- Brain Processes Underlying the Extinction and Reactivation of Fear Memories
-
In a study published in 2019 in the journal Nature Neuroscience, researchers funded by the National Institute of Mental Health investigated the neurobiological changes that occur in the brain circuits of mice when contextual fear memories — fear of a place where an aversive event occurred — are formed and extinguished.
- Fast-Fail Trial Shows New Approach to Identifying Brain Targets for Clinical Treatments
-
An innovative NIMH-funded trial shows that a receptor involved in the brain’s reward system may be a viable target for treating anhedonia (or lack of pleasure), a key symptom of several mood and anxiety disorders.
- Large-Scale Genetics Study Sheds Light on Developmental Origins of Autism
-
Researchers were able to identify different types of rare genetic variations associated with autism spectrum disorder by analyzing data shared via the NIMH-funded Autism Sequencing Consortium.
- Reading the Brain’s Map: Coordinated Brain Activation Supports Spatial Learning and Decision-Making
-
NIH-supported study finds that spatial “replay” in neurons may help rats learn how to navigate toward goals.
- New BRAIN Initiative Awards Accelerate Neuroscience Discoveries
-
The NIH has announced its continued support for the Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative by funding more than 180 new BRAIN Initiative awards, bringing the total 2019 budget for the program to more than $424 million.
- NIH BRAIN Initiative Tool May Transform How Scientists Study Brain Structure and Function
-
Researchers have developed a high-tech support system that can keep a large mammalian brain from rapidly decomposing in the hours after death, enabling study of certain molecular and cellular functions.
- Ketamine Reverses Neural Changes Underlying Depression-Related Behaviors in Mice
-
Researchers have identified ketamine-induced brain-related changes that are responsible for maintaining the remission of behaviors related to depression in mice — findings that may help researchers develop interventions that promote lasting remission of depression in humans.
- Mega Docking Library Poised to Speed Drug Discovery
-
Researchers have launched an ultra-large virtual docking library expected to grow to more than 1 billion molecules by next year. It will expand by 1000-fold the number of such “make-on-demand” compounds readily available to scientists for chemical biology and drug discovery.
- Puerto Rico’s “Fear Lab” Mentors Neuroscience Rigor amid Diversity
-
A lineage of young neuroscientists from diverse backgrounds trace their scientific roots to a “fear lab” in Puerto Rico that the National Institutes of Health has been supporting for two decades.
- New Findings Reveal Surprising Role of the Cerebellum in Reward and Social Behaviors
-
A new study in rodents has demonstrated, for the first time, that the brain’s cerebellum plays a role in controlling reward and social preference behavior—findings that shed light on the brain circuits critical to the affective and social dysfunction seen across multiple psychiatric disorders.
- 2,000 Human Brains Yield Clues to How Genes Raise Risk for Mental Illnesses
-
PsychENCODE researchers are discovering the biological mechanisms by which mental illness risk genes work in the human brain.
- The Pathways Through which Light Affects Learning and Mood
-
In a new study, researchers have traced the brain pathways responsible for the effects of light on learning and mood. The findings revealed that these effects are brought about by two different and distinct pathways from the retina into the brain.
- NIH BRAIN Initiative Debuts Cell Census of Mouse Motor Cortex – for Starters
-
NIH BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN) has debuted its first data release, which focuses on motor cortex. In a related development, researchers have discovered cellular secrets of key social behaviors – mating, parenting, and aggression – in mouse hypothalamus.
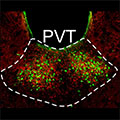
- Understanding Critical Components of the Brain’s Stress Circuitry
-
A new study has revealed more about the organization and function of a brain structure—the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus—that may serve a key role in linking stress detection to the development of adaptive behaviors.
- Bigger Human Brain Prioritizes Thinking Hub – at a Cost
-
Scientists have discovered that bigger human brains are organized differently than smaller ones.
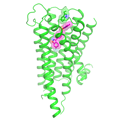
- Molecular Secrets Revealed: Antipsychotic Docked in its Receptor
-
Scientists have deciphered the molecular structure of a widely-prescribed antipsychotic docked in its key human brain receptor. The discovery may hold clues to designing better treatments for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and other mental illnesses.
- Memory Gene Goes Viral
-
A gene crucial for learning can send its genetic material from one neuron to another by employing a strategy commonly used by viruses.
- Brain’s Alertness Circuitry Conserved Through Evolution
-
Using a molecular method likely to become widely adopted by the field, researchers have discovered brain circuitry essential for alertness – and for brain states more generally.
- NIH BRAIN Initiative Builds on Early Advances
-
NIH has announced funding for 110 new awards totaling $169 million for the BRAIN Initiative.
- NIH BRAIN Initiative Launches Cell Census
-
The NIH today launched a major effort to discover and catalog the brain’s “parts list.”
- NIH Completes Atlas of Human DNA Differences that Influence Gene Expression
-
NIH researchers have completed an atlas documenting how DNA influence human gene expression.
- NIMH Releases Strategic Research Priorities Update
-
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) recently released its second annual update of the Strategic Research Priorities.
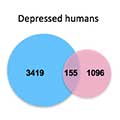
- Depression’s “Transcriptional Signatures” Differ in Men vs. Women
-
Brain gene expression associated with depression differed markedly between men and women. Such divergent “transcriptional signatures” may signal divergent underlying illness processes requiring sex-specific treatments.
- Breakthrough Method Yields Trove of Neuron Subtypes, Gene Regulators
-
Scientists have discovered a trove of neuronal subtypes by identifying their unique epigenomic signatures.
- Our Brains Harbor “Residual Echo” of Neanderthal Genes
-
Researchers have produced the first direct evidence that parts of our brains implicated in mental disorders may be shaped by a “residual echo” from our ancient past. The more a person’s genome carries genetic vestiges of Neanderthals, the more certain parts of his or her brain and skull resemble those of humans’ evolutionary cousins that went extinct 40,000 years ago.
- Webinar: RDoC - Fear & Anxiety: From Mechanisms to Implementation
-
This November 2016 RDoC webinar highlights the role of fear and anxiety in disorders such as phobias and depression.
- Scientists Replay Movie Encoded in DNA
-
For the first time, a primitive movie has been encoded in – and then played back from – DNA in living cells. It’s a major step toward a “molecular recorder” that may someday reveal secrets of the developing brain.
- NIH Names Winners of “Follow that Cell” Phase 2 Competition
-
Two biological engineering researchers are winners in Phase 2 of NIH’s Follow that Cell Challenge. The winners will share $400,000 in prizes awarded for development of new tools and methods for predicting the behavior and function of a single cell in complex tissue over time – and how that reflects the health of the tissue.
- Brain Circuit Tweak Wins Her Affection (if she’s a vole)
-
For the first time, neuroscientists have boosted a female rodent’s partnering with a male by stimulating connectivity of a brain reward circuit. Understanding the circuitry of such affiliative behaviors may lead to improved treatments for social impairment in severe mental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder.
- Connections Strengthen Within Specialized Networks as Brain’s Executive Function Matures
-
As we grow up, our brain’s specialized networks become more structurally segregated, contributing to improved executive functioning. These densely interconnected “modules” process information for key functions that underlie development of mental control and self-regulation.
- NIMH Grantee Wins One of Science’s Most Coveted Prizes
-
NIMH grantee Karl Deisseroth, M.D., Ph.D., of Stanford University, has been awarded one of science’s most generous prizes. A German foundation presented the inventor of technologies that are transforming neuroscience with its 4 million euros Fresenius Prize.
- NIMH to Host Multimodal Brain Stimulation Speaker Series
-
Beginning May 31, 2017, the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) will launch a speaker series intended to bring together leaders in the field conducting research using non-invasive brain stimulation and functional imaging including EEG, fMRI, and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS).
- Brain “Relay” Also Key to Holding Thoughts in Mind
-
Long overlooked as a mere “relay,” an egg-like structure in the middle of the brain also turns out to play a pivotal role in tuning-up thinking circuity. A trio of studies in mice are revealing that the thalamus sustains the ability to distinguish categories and hold thoughts in mind. It might even become a target for interventions for psychiatric disorders marked by working memory problems, such as schizophrenia.
- Human Forebrain Circuits Under Construction – in a Dish
-
Neuroscientists have created a 3D window into the human brain’s budding executive hub assembling itself during a critical period in prenatal development.
- Potential Source of HIV Persistence Confirmed
-
Scientists have shown that a class of immune cells not thought to be a primary reservoir for HIV can harbor the virus even following antiretroviral treatment (ART).
- Sleep May Trim Neural Connections to Restore Learning Ability
-
Sleep may be the price we pay for the ability to learn. It streamlines neural connections for optimal efficiency.
- Revealed: LSD Docked in its Human Brain Target
-
Scientists have discovered the molecular structure of LSD in its human brain receptor.
- Two NIMH Grantees Receive Prestigious Presidential Award
-
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) congratulates two NIMH grantees, Mary Kay Lobo from the University of Maryland School of Medicine and Eric Morrow from Brown University, who are among the 102 scientists and researchers receiving the 2017 Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE).
- NIMH Training Grant Recipient Wins Research Prize
-
NIMH training grant recipient Neir Eshel was named the 2016 Grand Prize winner of the Science & SciLifeLab Prize for Young Scientists for research related to the cellular basis of learning.
- Molecular Tool Parses Social Fear Circuit Intertwined with Aggression Hub
-
A genetic engineering tool has disentangled seemingly hopelessly intertwined brain circuits for social fear and aggression in mice.
- Worldwide Study Seeks to Unlock the Brain’s Genetic Code
-
Big data pinpoints genetic variation linked to brain volume and risk for disorders.
- NIMH’s Karen F. Berman, M.D. elected to National Academy of Medicine
-
At its annual meeting for 2016, the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) announced the election of 79 regular members, including the National Institute of Mental Health’s (NIMH Karen F. Berman, M.D. One of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine, election to the Academy recognizes outstanding professional achievement and commitment to service.
- NIH Nearly Doubles Investment in BRAIN Initiative Research
-
NIH’s third round of grants to support the goals of the Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Initiative total just over $150 million.
- NIMH Releases Strategic Research Priorities Update
-
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) recently released updates to its Strategic Research Priorities.
- How “Quickly Forgotten” Early Life Experiences Mature the Brain
-
Brain memory circuitry’s keen sensitivity to experience during an early critical period enables long-term memory ability to develop through practice.
- NIMH Grantees Named Recipients of Prestigious Kavli Prize
-
Three NIMH grantees have been named recipients of the 2016 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience.
- Connectome Map More Than Doubles Human Cortex’s Known Regions
-
Researchers have mapped 180 distinct areas on our brain’s cortex — more than twice the number previously known.
- Human Connectome Project Marks its First Phase
-
Studies based on a database made available by the Human Connectome Project’s first phase reveal that an individual’s brain connectivity can predict his or her behavior.
- Secrets to Our Smarts Hidden in the Folds of Our Cortex
-
The more folding in the thinking parts of our brain, the smarter we are – to a degree.
- Distractible Mice Offer Clues to Attention Deficit
-
A recent NIMH-funded study sheds new light on how the brain’s processing of sensory information, a key impairment in autism and ADHD, can affect higher level cognitive functions, such as attention and decision making.
- Circuit for Experience-Informed Decision-Making ID’d in Rats
-
Scientists have discovered secrets of how the brain recalls experiences of being in a particular location in making informed choices.
- A BRIGHT Technological Future for Mental Health Trials
-
Is mobile mental health research the next frontier for smartphones? Based on Dr. Patricia Areán’s pioneering BRIGHTEN study, research via smartphone app is already a reality.
- Experimental Combination Surprises with Anti-HIV Effectiveness
-
A compound developed by NIH-supported scientists to protect the nervous system from HIV surprised researchers by augmenting the effectiveness of an investigational antiretroviral drug beyond anything expected.
- Circuit Tweak Boosts Social Memory in Mice
-
Researchers have boosted the staying power of a social memory at least 80-fold by stimulating a circuit they discovered in mouse brain.