Science Updates About Schizophrenia
- Brain Connectivity Linked With Cognition in People With Early Psychosis
-
An NIMH-funded study identified consistent links between brain connectivity and cognitive function in people with early stage psychosis and people at high risk who later developed psychosis.
- Scientists Map Networks Regulating Gene Function in the Human Brain
-
An NIMH-funded research consortium has produced the largest and most advanced multidimensional maps of gene regulation networks in the brains of people with and without mental disorders.
- Study Reveals Potential Neural Marker for Social Impairment in Psychotic Disorders
-
Research funded by NIMH found a link between a low level of social interest among people with psychotic disorders and brain regions in the social motivation system.
- RAISE-ing the Standard of Care for Schizophrenia: The Rapid Adoption of Coordinated Specialty Care in the United States
-
• 75th Anniversary
The Recovery After an Initial Schizophrenia Episode research initiative, launched by NIMH to test the effectiveness of coordinated specialty care to treat first-episode psychosis, has transformed the mental health landscape in the United States and helped thousands of people with schizophrenia achieve better outcomes.
- Researchers Map the Genetic Landscape of Schizophrenia in the Brain
-
In a comprehensive postmortem genetic analysis of the caudate nucleus in the brain, NIMH-supported researchers identified many genes associated with schizophrenia risk, including a gene that regulates the flow of the chemical messenger dopamine.
- Computational Methods Identify Psychosis Symptoms in Spoken Language
-
Researchers used computational methods to automatically detect abnormalities in spoken language that could be used to predict symptoms of psychotic disorders including schizophrenia.
- Clinical Decision Support System Reduces Cardiovascular Risk in Patients With Serious Mental Illness
-
A new study shows the use of a clinical decision support system to prompt the use of shared decision-making tools, such as handouts, may result in positive impacts on long-term cardiovascular health in patients with serious mental illness.
- Gene Readouts Contribute To Distinctness of Mental Disorders
-
A new study conducted by researchers at NIMH suggests that differences in the expression of gene transcripts – readouts copied from DNA that help maintain and build our cells – may hold the key to understanding how mental disorders with shared genetic risk factors result in different patterns of onset, symptoms, course of illness, and treatment responses.
- NIH Initiative Expands Access to Resources for Early Psychosis Treatment and Research
-
The Early Psychosis Intervention Network (EPINET), an NIMH initiative aimed at determining how to best provide treatment for individuals experiencing symptoms of early psychosis, is increasing access to resources for researchers, providers, and families through a growing network of research hubs and a new website.
- NIMH Part of Collaborative Effort to Advance Early Intervention for Individuals at Risk of Developing Schizophrenia
-
NIMH has joined with other NIH Institutes in launching an new Accelerating Medicines Partnership focused on advancing the development of better ways to identify and treat those at clinical high risk for psychosis.
- Schizophrenia Risk Gene Linked to Cognitive Deficits in Mice
-
Mice with an impaired version of one the few genes definitively linked to schizophrenia showed abnormalities in working memory, mimicking those commonly seen in schizophrenia patients.
- Gene Regulators Work Together for Oversized Impact on Schizophrenia Risk
-
Gene expression regulators work together to raise an individual’s risk of developing schizophrenia. Schizophrenia-like gene expression changes modeled in human neurons matched changes found in patients’ brains.
- NIH Announces Funding Awards for National Early Psychosis Learning Community
-
NIMH awarded six research grants for studies to develop a learning health care system for the treatment of early psychosis.
- Mental Health Research Centers Forge Collaborations – with ALACRITY
-
Mental health research center directors emerged from a recent meeting with a renewed commitment to help each other achieve their common mission – to transform care of children, adolescents and adults with severe psychiatric disorders.
- Neuromelanin-Sensitive MRI Identified as a Potential Biomarker for Psychosis
-
Researchers have shown that a type of magnetic resonance imaging — called neuromelanin-sensitive MRI (NM-MRI) — is a potential biomarker for psychosis. NM-MRI signal was found to be a marker of dopamine function in people with schizophrenia and an indicator of the severity of psychotic symptoms in people with this mental illness.
- New Findings Reveal Surprising Role of the Cerebellum in Reward and Social Behaviors
-
A new study in rodents has demonstrated, for the first time, that the brain’s cerebellum plays a role in controlling reward and social preference behavior—findings that shed light on the brain circuits critical to the affective and social dysfunction seen across multiple psychiatric disorders.
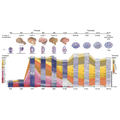
- 2,000 Human Brains Yield Clues to How Genes Raise Risk for Mental Illnesses
-
PsychENCODE researchers are discovering the biological mechanisms by which mental illness risk genes work in the human brain.
- Studies Support Use of Team-Based Care for Early Psychosis
-
Two recent studies add to the evidence that team-based early intervention services are feasible in real-world health care settings and result in improved outcomes for patients.
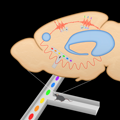
- Hyperconnectivity in a Brain Circuit May Predict Psychosis
-
NIMH-funded scientists have discovered a pattern in the way a brain circuit works that may help predict the onset of psychosis. High levels of chatter, or “hyperconnectivity,” in a circuit involving the cerebellum, thalamus, and cortex emerged as a potential “neural signature” in a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study.
- Inflammation in Pregnant Moms Linked to Child’s Brain Development
-
High levels of maternal inflammation during pregnancy have been linked to effects in children, including reduced brain circuit communications and altered long-distance brain wiring at birth, poorer cognitive function at one year – and to reduced impulse control and working memory at two years.
- Suspect Molecules Overlap in Autism, Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder
-
Depression, schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder share some of the same patterns of suspect gene expression – molecular signatures.
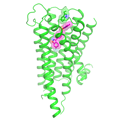
- Molecular Secrets Revealed: Antipsychotic Docked in its Receptor
-
Scientists have deciphered the molecular structure of a widely-prescribed antipsychotic docked in its key human brain receptor. The discovery may hold clues to designing better treatments for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and other mental illnesses.
- Scientists Give Star Treatment to Lesser-Known Cells Crucial for Brain Development
-
Star-shaped support brain cells, astrocytes, growing in 3-D “organoids” in a dish develop similarly as those in human brain tissue.
- Patient-Derived Support Cells Stunt Mouse Brain Development
-
Support cells generated from patients with childhood onset schizophrenia stunted neural circuit development when grafted into developing mouse brains.
- Our Brains Harbor “Residual Echo” of Neanderthal Genes
-
Researchers have produced the first direct evidence that parts of our brains implicated in mental disorders may be shaped by a “residual echo” from our ancient past. The more a person’s genome carries genetic vestiges of Neanderthals, the more certain parts of his or her brain and skull resemble those of humans’ evolutionary cousins that went extinct 40,000 years ago.
- Brain “Relay” Also Key to Holding Thoughts in Mind
-
Long overlooked as a mere “relay,” an egg-like structure in the middle of the brain also turns out to play a pivotal role in tuning-up thinking circuity. A trio of studies in mice are revealing that the thalamus sustains the ability to distinguish categories and hold thoughts in mind. It might even become a target for interventions for psychiatric disorders marked by working memory problems, such as schizophrenia.
- Estrogen Alters Memory Circuit Function in Women with Gene Variant
-
Brain scans reveal that fluctuations in estrogen can trigger atypical functioning in a key brain memory circuit in women with a common version of a gene. Since working memory function is often disturbed in mental disorders, such gene-hormone interactions are suspect mechanisms that may confer risk.
- Higher Death Rate Among Youth with First Episode Psychosis
-
A new study shows that young people with first episode psychosis have a much higher death rate than previously thought. Researchers looked at people aged 16-30 and found that the group died at a rate at least 24 times greater than the same age group in the general population.
- Powered-Up Probe ID’s Schizophrenia Genes That Stunt Brain Development
-
Scientists have pinpointed several schizophrenia-related gene variants that alter expression of other genes in illness-implicated circuitry of the human brain.
- Schizophrenia, Autism Risk Gene Trajectories Point to Shared Causes
-
Schizophrenia, autism risk gene trajectories point to shared causes
- Circuit for Experience-Informed Decision-Making ID’d in Rats
-
Scientists have discovered secrets of how the brain recalls experiences of being in a particular location in making informed choices.
- Team-based Treatment for First Episode Psychosis Found to be High Value
-
Coordinated Specialty Care for First Episode Psychosis is Cost Effective
- Schizophrenia’s Strongest Known Genetic Risk Deconstructed
-
Versions of a gene linked to schizophrenia may trigger runaway pruning of the teenage brain’s still-maturing communications infrastructure.The gene switched on more in people with the suspect versions, who faced a higher risk of developing the disorder.